info@suryaeyecare.com
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases which result in damage to the optic nerve, progressive and irreversible vision loss.
Glaucoma has been called the "silent thief of sight" because the loss of vision usually occurs slowly over a long period of time.
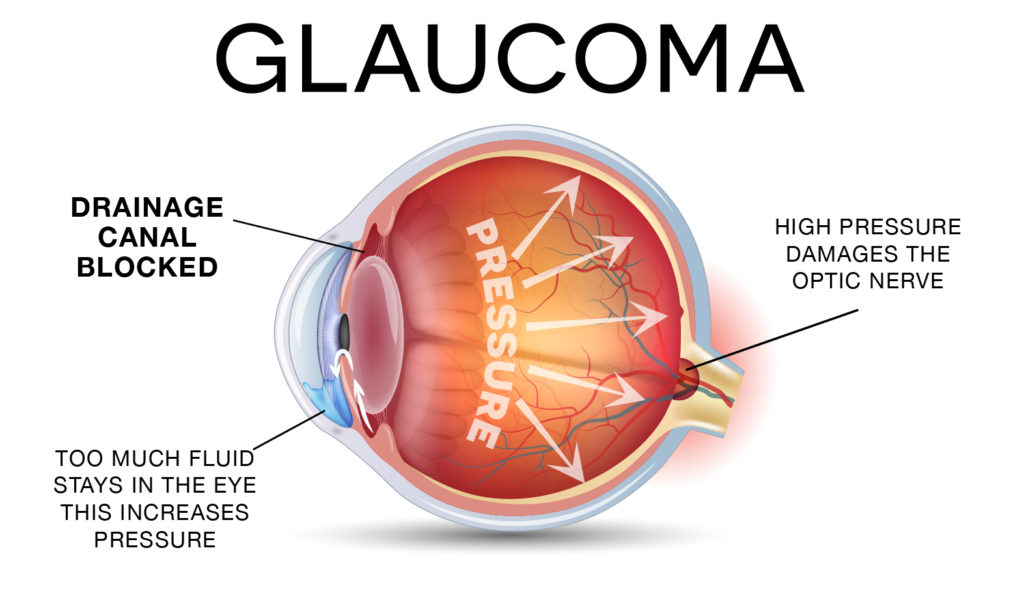
the result of high fluid pressure inside the eye. This happens when the fluid in the front part of the eye doesn't circulate the way it should.
Normally, the fluid, called aqueous humor, flows out of the eye through a mesh-like channel. If this channel gets blocked, the liquid builds up. That’s what causes glaucoma. The reason for the blockage is unknown and multifactorial.
One of the causes is Inheritance.
Less common causes include a blunt or chemical injury to the eye, severe eye infection, blocked blood vessels inside the eye, post surgical and inflammatory conditions.
TYPES OF GLAUCOMA
1. Open-angle glaucoma
2.Closed-angle glaucoma and
3. normal-tension glaucoma.
Open-angle glaucoma develops
1. Slowly over time without any warning signals and there is no pain.
2. It does not have acute attacks.
3. Blind spots begin to appear in the peripheral vision.
4. Side vision may begin to decrease followed by central vision resulting in blindness if not treated.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS:
The lack of clear symptoms make screening via regular eye check-ups important.
The only signs are
1.Gradually progressive visual field loss,
2.Optic nerve changes (increased cup-to-disc ratio on fundoscopic examination).
CLOSED ANGLE GLAUCOMA
Angle-closure glaucoma. It’s less common in the West than in Asia.
Also called acute or chronic angle-closure or narrow-angle glaucoma.
The eye doesn’t drain right because the angle between the iris and cornea is too narrow.
The iris is usually in the way.
This can cause a sudden buildup of pressure in the eye.
It’s also linked to farsightedness and cataracts
Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly.
When it occurs suddenly its called Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma
About 10% of people with closed angles present with acute angle closure characterized by
sudden ocular pain,
seeing halos around lights,
red eye,
very high intraocular pressure (>30 mmHg),
nausea and vomiting,
sudden decreased vision, and a
fixed, mid-dilated pupil.
Acute angle closure is an emergency.
Closed-angle glaucoma also presents gradually
Vision loss from glaucoma, is irreversible.
INVESTIGATIONS:
The only sure way to diagnose glaucoma is with a complete eye exam. A glaucoma screening that only checks eye pressure is not enough to find glaucoma.
Any signs of deterioration, including loss of nerve tissue during follow ups is also an essential part in aiding the diagnosis.
A detailed medical history:
The symptoms experienced by the patient, family history of glaucoma if present, Systemic conditions like Diabetes, Hypertension, Bronchial Asthma also is important in diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma.
During a glaucoma exam, it is essential to
◦ measure the eye pressure (Applanation Tonometry)
◦
◦ inspect the eye’s drainage angle
◦ examine the optic nerve for damage
(CUP/DISC RATIO)
◦ test the peripheral (side) vision (PERIMETRY)
◦ take a picture or computer measurement of the optic nerve (OCT)
◦ measure the thickness of the cornea (Pachymetry)
TREATMENT:
The treating doctor would prescribe eye drops, advise a laser surgery, or microsurgery.
Eye drops
These either reduce the formation of fluid in the eye or increase its outflow. Side effects may include allergies, redness, stinging, blurred vision, and eyes. Some glaucoma drugs may affect the heart and lungs.
Laser surgery
This procedure can slightly increase the flow of the fluid from the eye for people with open-angle glaucoma. It can stop fluid blockage if there is angle-closure glaucoma. Procedures include
• Trabeculoplasty: Opens the drainage area
• Iridotomy: Makes a tiny hole in the iris to let fluid flow more freely
• Cyclophotocoagulation: Treats areas of the middle layer of your eye to reduce fluid production
Microsurgery
In a procedure called trabeculectomy, the doctor creates a new channel to drain the fluid and ease eye pressure. Sometimes this form of glaucoma surgery fails and has to be redone. The doctor might implant a tube to help drain fluid. Surgery can cause temporary or permanent vision loss, as well as bleeding or infection.